Table of Contents
Modified Search Queries Based on Misspellings and Synonyms
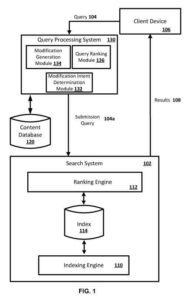
This patent is about ranking modifications of a previous query based on a current query.
Internet search engines provide information about Internet accessible documents such as web pages, images, text documents, and multimedia content. A search engine may identify the records in response to a searcher’s search query that includes search terms. The search engine ranks the documents based on the relevance of the documents to the query and the importance of the papers and provides search results that include aspects of and links to the identified records.
Related Content:
- Technical SEO Agency
- Ecommerce SEO Agency
- Shopify SEO Services
- Franchise SEO Agency
- Enterprise SEO Services
The searcher’s search query may be modified and used in identifying SERPs.
Search Query misspellings may be corrected to create modified search queries to identify the documents.
Search Query Synonyms may get used in creating modified search queries, and such modified search queries may be used to identify documents.
The present disclosure gets directed to methods and apparatus for ranking modifications of a previous query. For example, changes of an earlier query may be generated based on a current query issued after the last query.
For example, modifications of the previous query may be generated based on substituting n-grams of the last query with n-grams of the current query.
For example, the previous query may be [weather tomorrow], and the current query may be [how about on tuesday]. Modifications of the last query may be generated by substituting the n-gram “Tuesday” with each term of the previous query to form the changes [tuesday tomorrow] and [weaTuesdayesday].
Modifications of the previous query may additionally and alternatively get generated by substituting the n-gram “on Tuesday” with each term of the last query to form the changes [on Tuesday tomorrow], [weTuesdayn tuesday]. Each modification may be identified, and a ranking of each of the changes may be determined.
At least one of the modifications may get selected as a submission query based on the rankings of the modifications. The desired change may be submitted instead of, or in addition to, the current query.
How Modified Search Queries May Take Place
A computer-implemented method may get provided that includes the steps of:
- Receiving a current query including many current query terms
- Deciding on, based on of the current query terms, that the current query is indicative of an intent of the searcher to refine a query
- Picking a previous query associated with the current query, the last query including a plurality of prior query terms and issued before the current query by at least one of a computing device and a searcher that gave the current query
- Choosing a modification n-gram based on the current query terms
- Generating modifications of the previous query that each includes the modification n-gram substituted in the prior query terms
- Identifying, for each modification of multiple of the modifications
- A popularity measure and a related concept measure, where the popularity measure is indicative of the popularity of the modification and the related concept measure is indicative of a likelihood of co-occurrence
- In documents of the modification n-gram and the previous query terms replaced by the modification n-gram in the modification
- Determining a ranking for each of the modifications gets based on the popularity measure for the modification and the related concept measure of the modification
- Selecting one modification of the modifications to utilize as a submission query when the ranking of the one modification is more prominent than at least the rankings of the other modifications
Modifying search queries may include the following features.
- Submitting one modification to a query system in place of the current query. The query system may be a search system, and the method may further include: determining search results responsive to the one modification; and providing the search results to the searcher.
- Determining, for at least a first modification of the modifications, a query pattern of the first modification, wherein the popularity measure for the first modification includes a query pattern popularity measure indicative of the popularity of the query pattern of the first modification. Determining the query pattern of the first modification may consist of: selecting a category of an n-gram in the first modification and substituting the n-gram with an identifier of the class.
- Ranking of the modification may get boosted when the modification n-gram of the transformation and the previous query terms replaced by the modification n-gram in the change indicate geographic locations.
The modified search results may further include:
- Identifying a current query popularity measure indicative of the popularity of the current query based on previous queries
- Choosing a ranking for the current query based on the current query popularity measure, wherein selecting the one modification of the modifications to utilize as a submission query occurs only when the ranking of the one transformation is more prominent than the ranking for the current query.
- Select the current query to utilize as the submission query when the ranking for the current query is more prominent than the rankings of the other modifications.
- Boosting the ranking of the current query, where the boost promotes the ranking of the current query relative to the modifications.
- Utilizing a default measure for the current query for the related concept measure of the current query
- Picking the ranking for the current query based on the default measure.
- The previous query and the current query may be provided via spoken input of the searcher. Determining the current query indicates a potential intent to refine the previous query based on the last query and the current via spoken information of the searcher.
- Determining the current query is indicative of a potential intent of the searcher to refine the previous query may get based on determining the current question includes refinement intent n-grams.
The modified search queries behind the patented can also include:
- Finding a second modification n-gram based on the current query terms
- Generating additional modifications of the previous query that each includes the second modification n-gram substituted for of the previous query terms
- Identifying the popularity measure and the related concept measure for each of multiple of the additional modifications
- Determining a ranking for each of the multiples of the additional modifications, based on the popularity measure for the further modification and the related concept measure of the further modification
- Selecting the one modification of the modifications to utilize as a submission query occurs only when the ranking of the one transformation is also more prominent than the rankings of the additional improvements.
- Deciding that a matching one of the additional modifications includes the same terms in the same order as a matching one of the modifications
- Calculating a combined ranking of the matching one of the additional modifications and the matching one of the modifications, the combined ranking being more prominent than an individual ranking of either of the matching one of the different modifications.
A computer-implemented method may be provided that includes the steps of:
- Receiving a current query including a plurality of current query terms
- Choosing, based on the current query terms, that the current query is indicative of an intent of the searcher to refine a query; determining a modification n-gram based on the current query terms
- Generating modifications of the previous query that each includes the change n-gram substituted in the prior query terms
- Finding candidate queries, the candidate queries including multiple of the generated modifications and including the current query
- Identifying, for each candidate query of the candidate queries: a popularity measure
- Wherein the popularity measure is indicative of the popularity of the candidate query based on previous queries.
- Determining a ranking of each candidate query, wherein the ranking of a given candidate query is based on the popularity measure for the given candidate query.
- Selecting one candidate query of the candidate queries to utilize as a submission query, the selecting based on the ranking of the one candidate query.
The modified search queries patent is at:
Ranking modifications of a previous query
Inventors: Bruce Christensen, Kumar Pravir Gupta, and Jan Kuipers
Assignee: GOOGLE LLC
US Patent: 11,169,989
Granted: November 9, 2021
Filed: October 13, 2015
Abstract
Methods and apparatus related to ranking modifications of a previous query.
For example, modifications of a previous query may be generated based on a current query issued subsequent to the previous query by substituting n-grams of the previous query with n-grams of the current query. measures of each of the modifications may be identified and, based on such measures, a ranking of each of the modifications may be determined.
One of the modifications may be selected as a submission query based on the rankings of the modifications.
The submission query may be selected for submission in lieu of, or in addition to, the current query.
Modified Search Queries Conclusion
I have summarized the summary of the patent, and if you want to try to learn more about how it works, you may want to click through to see the whole patent. There have been many patents from Google that involve rewriting search queries to correct misspellings or provide synonyms so that very similar meaning search results are received by a searcher.
I wanted to include links to some posts that are about providing those synonyms because there are a number of different ways that Google may choose to provide those to searchers. Many of the modified search queries patents involving synonyms first started appearing at Google around 2003, and have evolved to synonym substitutions involving hummingbird and RankBrain. One way that Google refers to modified search queries is rewriting queries. Google has been modifying queries for a long time, and these are some examples of posts about Google doing that:
5/25/2007 – Using a Local Category Synonym to Refine Queries
12/29/2008 – How a Search Engine Might Use Synonyms to Rewrite Search Queries
12/22/2009 – Google Search Synonyms Are Found in Queries
1/19/2010 – Google Synonyms Update
2/16/2011 – More Ways Search Engine Synonyms Might be Used to Rewrite Queries
8/12/2013 – How Google May Substitute Query Terms with Co-Occurrence
9/27/2013 – The Google Hummingbird Update and the Likely Patent Behind Hummingbird
10/27/2015 – Investigating Google RankBrain and Query Term Substitutions
12/21/2015 – How Google Might Make Better Synonym Substitutions Using Knowledge Base Categories
8/23/2019 – How Google May Do Query Rewriting by Looking at a Searcher’s Prior Queries
9/27/2021 – Rewritten Queries and User-Specific Knowledge Graphs
Search News Straight To Your Inbox
*Required
Join thousands of marketers to get the best search news in under 5 minutes. Get resources, tips and more with The Splash newsletter: